Understanding Debentures: A Comprehensive Guide on its Issuance, Challenges, Compliances & Rights of Holders
Debentures are one of the most popular debt-financing instruments in the Indian capital market primarily for raising long term funds. They offer a structured way for companies to secure the required funds for their businesses without diluting the equity ownership of the entity, while providing the investors with an opportunity that is relatively secure to generate fixed income. However, a complex web of regulatory regimes, taxations and accounting standards exist that requires to be navigated in order to manage the process of issuing of debentures in India. This article explores the step-by-step process of issuing debentures in India, addressing the challenges involved, compliance requirements, and safeguarding debenture holders' rights.
1. Understanding Debentures and the Process of Issuance
A debenture is a debt instrument issued by companies or governments to raise funds. It can be secured or unsecured, depending on whether it is backed by collateral. Secured debentures are supported by specific movable or immovable assets, ensuring repayment to the debenture holders. These securities often comply with the conditions set out in Rule 18 of the Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014. An unsecured debenture, on the other hand, is not backed by any collateral and is solely to be relied on the basis of the market reputation and creditworthiness that the issuer has got.
Debentures are flexible instruments that can be:
Convertible, allowing conversion into shares, or
Non-convertible, offering fixed returns based on the terms of agreement.
Partly Convertible Debentures, which comprise of convertible and non-convertible portions where the convertible portion is converted into equity shares whereas the non-convertible portion is redeemed at the expiry of the term specified.
Debentures must be adequately charged as per deposit rule and if not charged, it must be compulsorily convertible within 10 years. In case it’s not charged or convertible, it is not considered to be a deposit, and the company needs to comply with the deposit rules. However specific exemptions are given to a few private companies.
Debentures are issued as per Section 71 of the Companies Act, 2013 read with Rule 18 of the Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014 and are regulated by SEBI if the debentures are issued by listed companies.
The process for issuing debentures through private placement starts with obtaining a valuation report from a registered valuer and then is followed by subsequent steps outlined below.
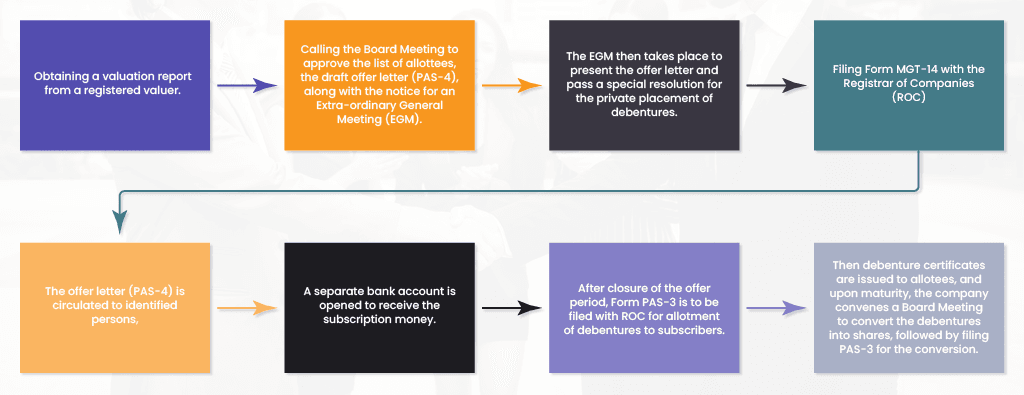
Companies also need to appoint debenture trustees, in case debentures are to be issued to more than 500 persons for subscription of its debentures. Further, the company is also required to create a Debenture Redemption Reserve for the purpose of redemption of debentures.
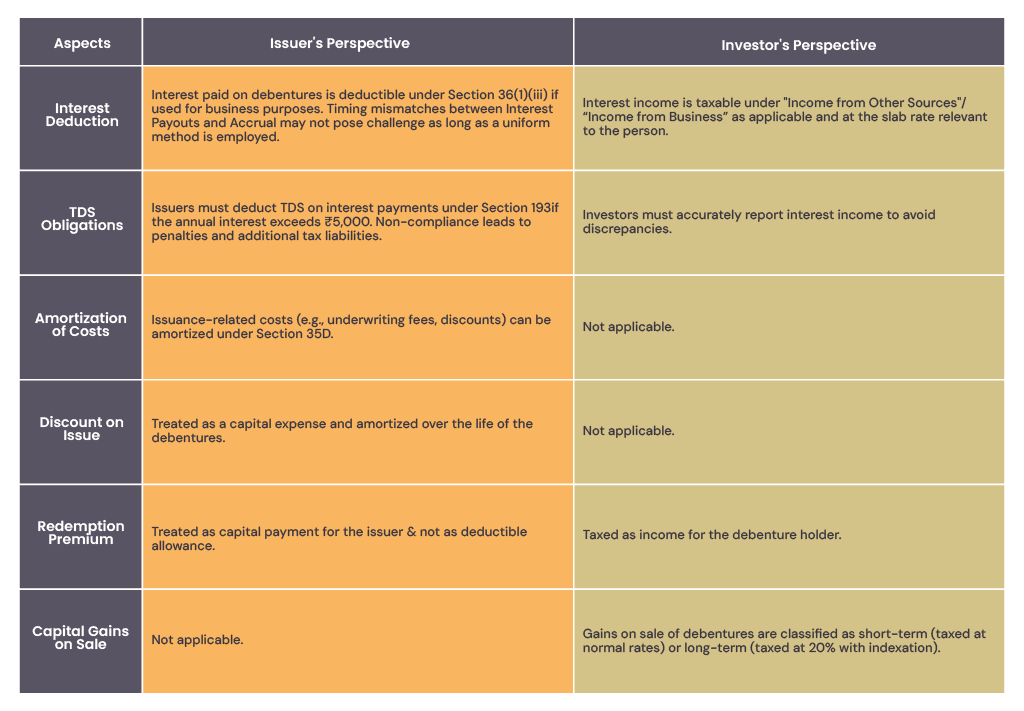
2.Taxations on Debentures
Debentures hold specific implications of Taxation on both the issuer as well as on investors. Debentures are subject to the provisions of the Income Tax Act, 1961, with respect to interest payments, issuance discounts and redemption premiums. Let’s have a quick look at various implications of debentures from a taxation perspective.
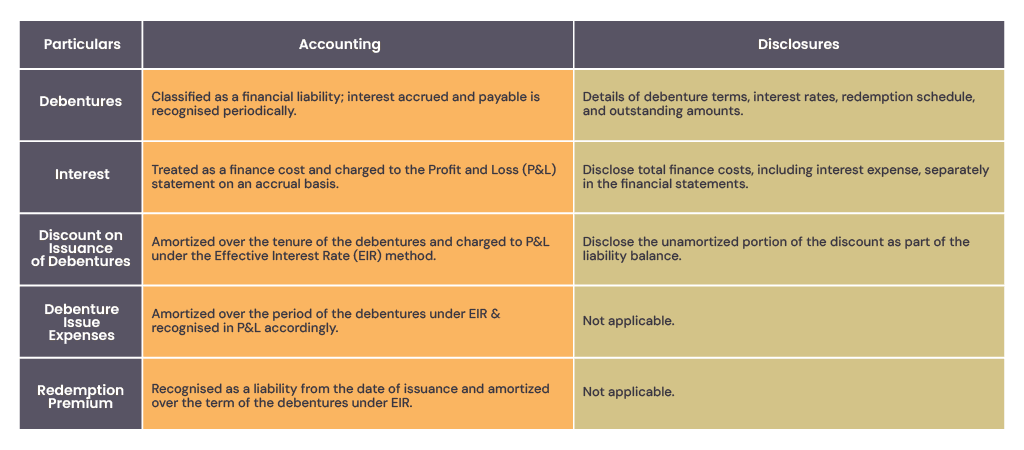
3.Disclosures and Reporting of Debentures
Disclosure and reporting of debentures focus on ensuring an accurate representation of financial liabilities, expenses, and tax effects related to debentures in the financial statements. Here’s a brief on accounting and reporting of various particulars related to debentures under Accounting Standard (AS 22) and Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS 12).
4. Debentures and FEMA Compliance
Debentures issued to foreign investors are subject to strict compliance under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999. Key provisions include
Adherence to External Commercial Borrowing (ECB) guidelines
Sectoral caps, end-use restrictions, and pricing norms.
Filing of FC-GPR to RBI through authorized dealer (AD) bank is required where foreign investors are involved.
In case of Non-convertible debentures or optionally convertible debentures, companies must report transactions through form ECB-2 to RBI through the authorized dealer bank. Delays in reporting or improper fund utilization may result in penalties.
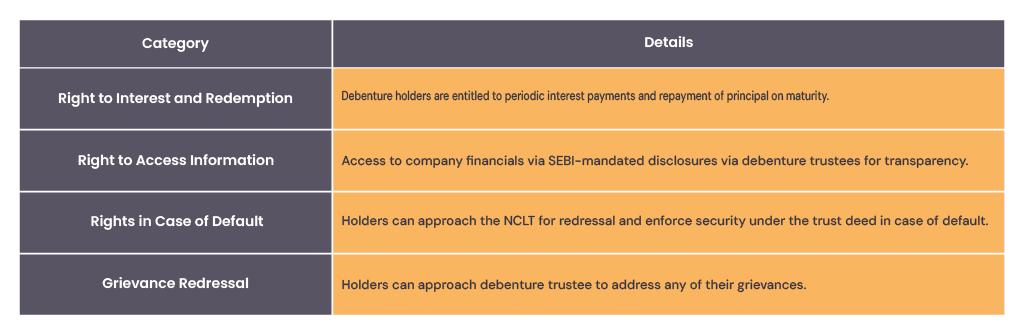
5.Rights of Debenture Holders
Debenture holders of a company are granted certain rights to protect their interests. Some of these specific rights are listed below:
Conclusion
Debentures provide a leveraged way for businesses to raise funds, offering fixed returns to their investors. However, it’s imperative for the companies to carefully navigate various regulatory, accounting and taxation conditions, including those such as adherence to FEMA regulations. Therefore, proper monitoring and management of issuance, disclosures and reporting is a must for debentures.
On the other hand, understanding the debenture holders’ rights and the obligations are crucial for the investors to safeguard their own interests. Availing professional help and expertise can help businesses maximize the benefits of debentures as a form of Fund raising while ensuring Compliance standards are also met.
Contributors
Nikita Mittal linkedin
CA Prajwal Bhat linkedin
CA Sindhushree M linkedin
Kuldeep Sarma linkedin
Poonam Vernekar linkedin

